Looking to lower your electricity bill? It starts with understanding when and how you use electricity. By reviewing your energy usage, you can spot the times when you use the most power and which appliances consume the most. This information is key to cutting costs.
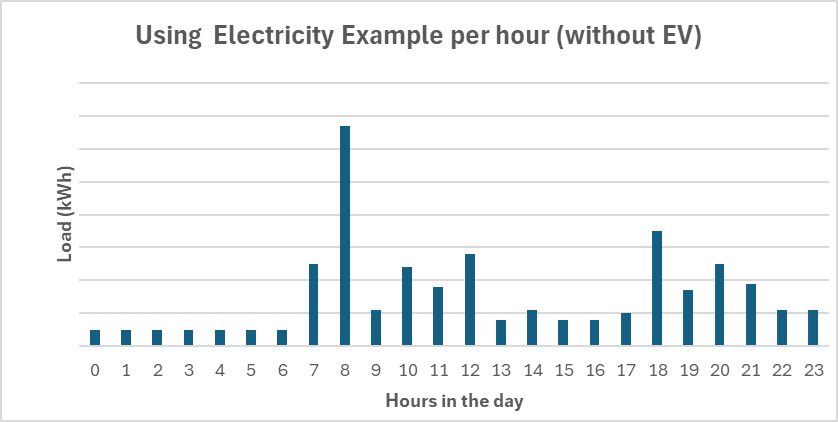
Below is an example that shows how much electricity a household uses each hour. The taller the bar, the more energy is used during that hour. You can see a spike around 8 AM, likely because people are getting ready for work or school. In contrast, early morning hours, when the household is asleep, show much lower energy use. This example might also reflect a home using efficient heating during winter, resulting in lower usage overnight.
Cut Costs with Time-of-Use Rates
Think of the electricity grid like a busy road. During rush hour, traffic slows down because everyone is on the road at the same time. The same thing happens with electricity—during peak hours (like afternoons and early evenings), lots of people are using power, which puts stress on the grid.
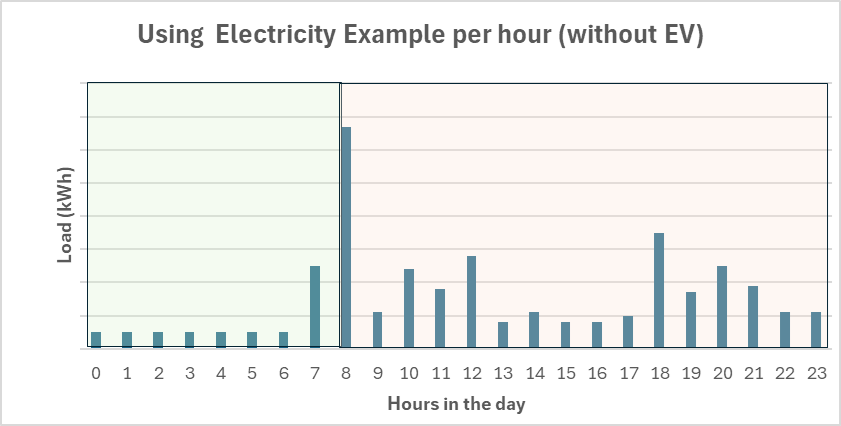
In the chart below, you’ll see the household’s energy use in two colors: green and orange. Green represents times when electricity is cheaper, while orange shows when it’s more expensive. As you can see, most of the electricity is being used during the orange (expensive) hours. If the household shifted some tasks, like running the washing machine, dryer, or dishwasher, to the green (cheaper) times, they could save money. Even small changes like this can make a big difference on their electricity bill.
Understanding Time-of-Use Tariffs for Electricity
Some utility companies offer plans that charge you based on when you use electricity. The rates vary depending on the time of day—electricity is cheaper during certain hours and more expensive during others. By understanding how these time-of-use tariffs work, you can adjust your habits and save money on your electric bill.
Why Do Power Companies Offer Variable Electricity Rates?
Variable electricity rates work like offering different prices to drive on the roads at different times of day. When more people use the roads at quieter times, traffic flows smoothly. Similarly, when more people use electricity during off-peak hours (when the grid is less busy), it helps utility companies avoid overloads and keep the system running smoothly.
By charging higher rates during peak hours, utility companies encourage people to shift their energy use to less busy times. This reduces strain on the grid and helps prevent blackouts or other issues during periods of high demand—like when everyone is cooking dinner or watching TV. During off-peak times, such as late at night when most people are asleep, electricity is cheaper because demand is lower.
This pricing system, known as Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs, means that electricity costs vary throughout the day, giving you the opportunity to save money by using energy during cheaper, off-peak hours.
Example: How Variable Rates Can Save You Money
Let’s look at an example to show how time-of-use tariffs can impact your electricity bill. We’ll compare two scenarios: one where a household uses a variable rate plan, and another where they don’t. In both cases, the household uses 150 kWh of electricity in a month, so the only difference is the plan they’re on. This will help illustrate how using the same amount of energy can cost less when you take advantage of variable rates.
A Time-of-Use Electricity Tariff
For this example, let’s assume that electricity costs €0.18 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) during the day, from 8 AM to midnight. At night, from midnight to 8 AM, the cost drops to €0.10 per kWh.
Now, if your total electricity usage for the month is 150 kWh, and you use 100 kWh during the day and 50 kWh at night, your electricity bill would be calculated like this:
- Daytime usage: 100 kWh x €0.18/kWh = €18
- Nighttime usage: 50 kWh x €0.10/kWh = €5
- Total bill: €18 + €5 = €23
Without a Variable Rate for Electricity
If there’s only one flat rate for electricity throughout the day, the cost is often higher. Let’s say the rate is €0.21 per kWh. In this case, the family’s monthly bill would be:
- Total bill: 150 kWh x €0.21 = €31.50
As you can see, the household with a time-of-use plan pays less (€23) compared to the flat-rate plan (€31.50). This shows that variable rates can save you money, even though the peak-time rates are sometimes higher than a flat rate.
What can you do?
If your utility provider offers time-of-use or variable tariffs, where you pay less during certain times of the day, here are some steps you can take to maximize your savings:
- Install a Smart Meter: A smart meter tracks your electricity use hour by hour, so you can see exactly when and how much energy you’re using. Many utility companies offer free installations, giving you better control over your energy habits.
- Adjust Your Daily Habits: Shifting energy-heavy tasks like laundry or dishwashing to off-peak hours can significantly reduce your bill. Even small changes can add up over time.
- Monitor Your Usage: If your utility offers an app or online portal, check your electricity usage regularly. Look for patterns and try to match high energy use with specific activities (e.g., running the washing machine). This helps you identify when to shift energy use to cheaper times.
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: When it’s time to replace appliances, choose energy-efficient models. These not only use less electricity but can save even more if run during off-peak hours.
- Use Smart Appliances: Some appliances can be programmed to run during off-peak times automatically. Set them to start when rates are lower, and enjoy the savings without having to think about it.
- Install a Programmable Thermostat: Adjust your thermostat to lower the temperature during peak hours to reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Invest in Energy Monitoring Devices: These devices show real-time energy usage, helping you identify which appliances are using the most electricity. With this information, you can turn off unnecessary devices or shift their use to cheaper times.
Taking these simple steps can help you cut costs and make the most of your time-of-use tariff plan.
In conclusion, saving on your electricity bill is easier than you might think. By simply shifting your energy use to off-peak hours and being mindful of when and how much electricity you use, you can make a big difference in your monthly costs. Small adjustments, like running appliances at cheaper times or using energy-efficient devices, can lead to significant savings over time. With just a little effort and smarter energy habits, you’ll not only reduce your bill but also take control of your household’s energy use.