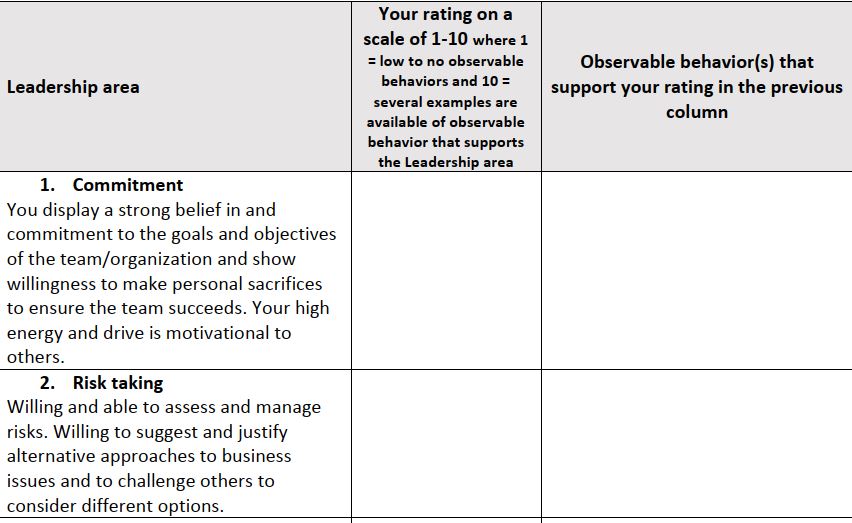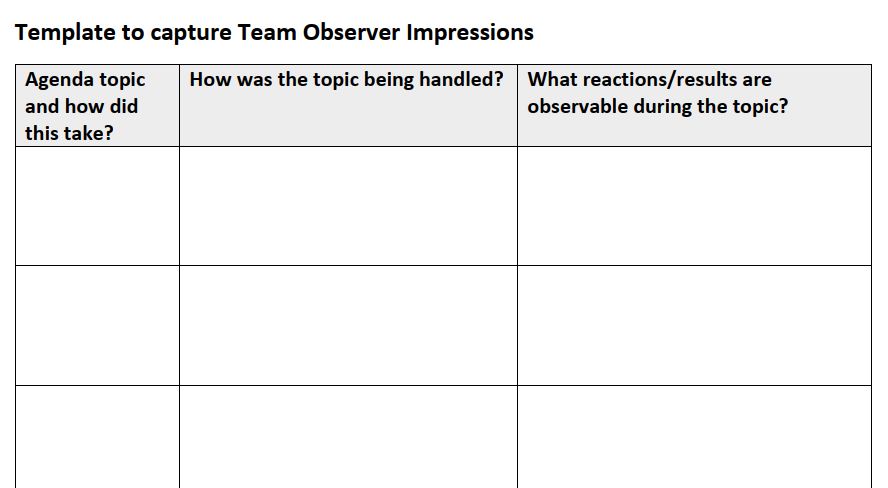
I am a strong believer in experiential learning – learning by or based on an experience and observation. Key learning points seem to be integrated faster and stronger when the learners are put in a situation where the skills they need to learn or apply are put to the test.
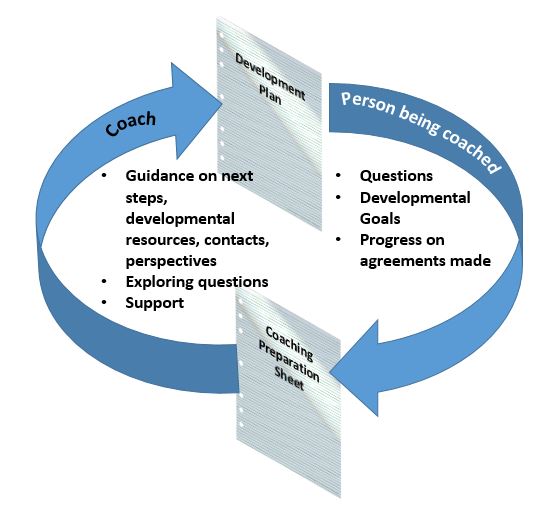
The exercise I am sharing (see download file below) is a group or team exercise focused on the style of a leader and how a leader approaches employee issues given their own background and preferences. The backdrop for the experience could be situational leadership or Emotional Intelligence for leaders. It is up to the trainer or facilitator to choose the right materials to suit the needs of the team or group.

The exercise requires some volunteers to engage in role-play based on specific scripts – included in the resource. There are “role sheets” to help those standing in as employees understand how that employee behaves and describes his or her style.
The key to this exercise is to showcase the possible dilemmas that leaders can face when confronted with employee behavior that seemingly goes against their own values or goals at work. The discussion after the role-play exercises is where the most value can be realized. Reflecting on what the group saw and experienced during the role-play and then relating that to their day-to-day work-life is where most insights tend to surface. This helps each leader determine how he or she could adopt a new mindset in dealing with difficult discussions with employees going forward.
This exercise works well for groups ranging from 8 to 16 people. Larger groups of 20 people or more can work too, but you may need to add in an additional step – a small group exercise. In that case, divide the group into smaller groups of 4 or 5 people and have them discuss the exercise debrief questions in the small groups before requesting each of the small groups to report back to the larger group for further discussion. You may want to consider an additional facilitator to assist if you are dealing with groups larger than 20 people.
Without emotional intelligence or a compassionate approach to interpersonal relationships even leaders with the best technical minds and education will never be great leaders with motivated followers. Exercises like the resource I share here can help trainers and facilitators bring home the importance of having the right approach and encourage a personal change process in developing leaders.