The ability to reflect and learn from experiences and observations is one I most commonly associate with and admire in the best leaders that I have met over the years. This resource can be used to help leaders reflect on their own behaviors to identify development and improvement needs.
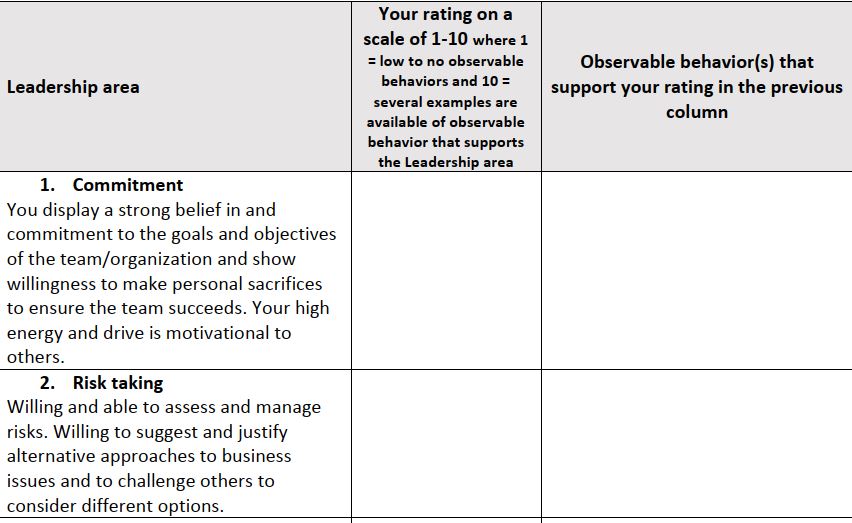
The leadership rating worksheet shared contains a sheet for self rating and also a sheet which can be shared with others for feedback purposes.
The resource (see downloadable file above) is not only helpful for leaders in rating themselves and uncovering possible developmental needs, but can also be used as a 360-type feedback tool. In that case the leader rates himself or herself and then requests feedback from others – in more senior roles, same level peers or in lower hierarchical roles – interacting with the leader on a regular basis. The 360 view can help eliminate any blind-spots that a leader may have concerning his or her own leadership behaviors as the perspectives are from others who often interface with the leader.
The leadership aspects covered in this resource are:
- Commitment
- Risk taking
- Motivational style
- Open-mindedness
- Diversity conscious
- Trustworthiness
- Continuous learning
- Self-adjustment
- Steadiness
Each of the aspects come with a brief description to ensure ratings are comparable after you have obtained feedback from others.
Uses for this resource include:
- Updating your own development plan and setting new goals and priorities for your own development activities
- Discussing the results with a coach or mentor to get guidance on what to focus on and how to plan next steps to improve on key leadership aspects.
- If a manager rates all of the leaders working in his or her department using this tool you can compare the leaders to each other in terms of strengths and development needs. This would be useful information to help select the best development programs for the team over the next year (for example).
Developing leadership skills is a lifelong journey. We can all learn to do better in some aspects over time and tools like this one can be a very useful check-in for reflection even for those who have been leaders for a long time. It is also true that we expect more from leaders in a globalized business world and concepts like “diversity conscious” and “cross cultural” skills are becoming very important for leaders to be effective on a global scale.