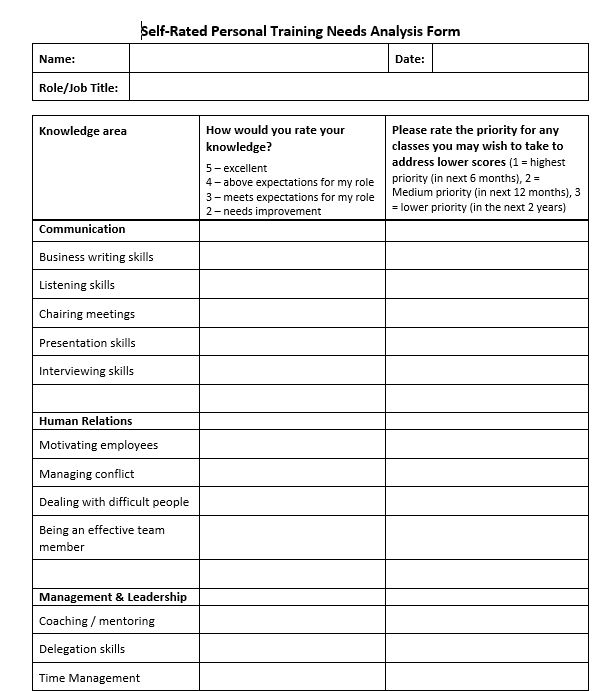
Delegation isn’t just about offloading work; it’s about developing your team’s potential. By strategically assigning tasks, you not only free up your time but also equip your employees with new skills and responsibilities. However, keeping track of who’s doing what can be challenging. That’s why a clear system for delegating and monitoring tasks is essential for maximizing productivity and employee growth. The template I am sharing is a great way to keep track of not only who is working on which delegated task, but also what was the overall purpose of the delegated task.
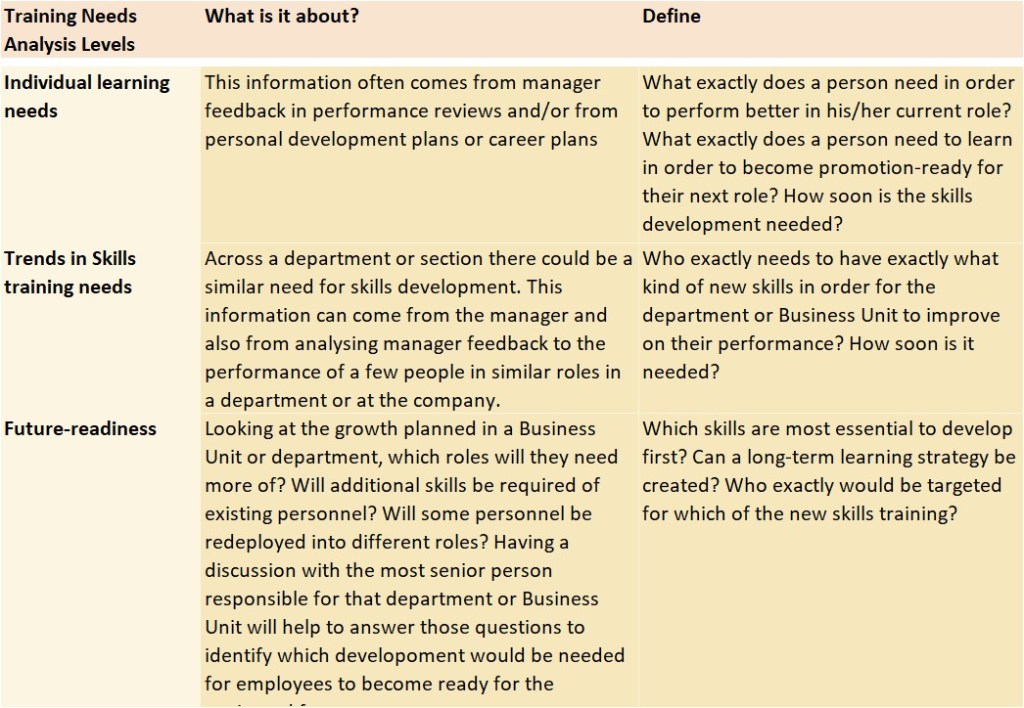
Try to match the task or activity/project you need to delegate to the right person in your team given their current skills and competencies and also matched to current development needs each of them have. The template is based on a list of categories to consider: (see second tab in template for the definitions shown below)

The delegation tracking sheet helps you keep track of the level of capability the person has – which uses the definitions above to help remind you how much support he or she might need with that task.

Use the drop down list in column B to select the category that applies to that task/project and the person that you are delegating to. You can create more lines for delegated tasks by just inserting a line between the existing lines.
Reasons why this list can be very useful:
- Keeping this list up to date and referring to it in a regular basis will help you remember when to check in on someone working on a delegated task or project.
- You keep track of the reasons why you gave a specific task to someone – from a developmental perspective. This means you know how much support and coaching may be needed while the person is working on this task.
- Avoid giving the same task to more than one person. There is nothing more demotivating to an employee than finding out another colleague is working on the exact same project as he or she is after having already spent several hours doing research and talking to people about the project in order to deliver a great result.
You can do more and accomplish more as a manager when you don’t have to rely on your memory alone to remember who is working on which tasks and projects for you.
Effective delegation is the cornerstone of successful management. By utilizing this template to track delegated tasks, managers can optimize workload distribution, identify development opportunities for team members, and ensure that projects stay on track. This proactive approach not only boosts productivity but also builds a culture of empowerment and growth within the team.