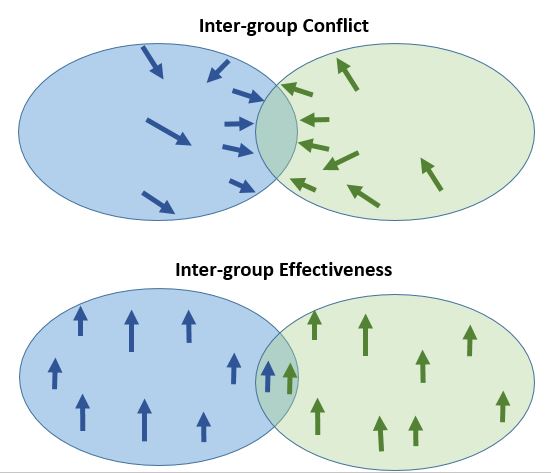
Your project team is very diverse and you are concerned that this may impact how your project will be executed – will you be able to achieve your overall project goals or will there be a lot of internal strife, misunderstandings and disagreements? Will they work against each other and have the wrong assumptions about each other and the project goals and metrics? If so, this team-building activity may help.
The downloadable resource I am sharing is a team activity you can use to help project team members understand that different groups of people can have different views on the various aspects of running a project and also the relative importance of key project processes. This activity makes those possible disconnects transparent which helps you lead clarification discussions with the team/group. While the activity itself is quite simple, the discussion that comes after the initial assignment is where the value lies and that will take up most of your time.
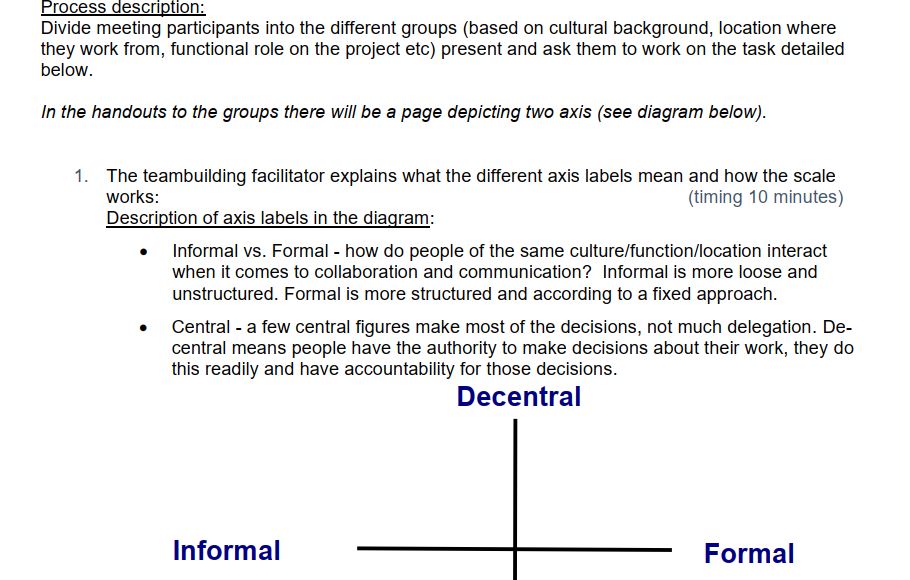
Further tips and ideas:
- You can segregate meeting participants in various ways related to the most important diversity aspects you wish to highlight within the team. As a variation you may choose to run the first part of the exercise more than once and each time segregating the group of participants in a different way. Options include: cultures, locations where they are from or live, level of life experience, function etc.
- There are several topics listed for discussion towards the end and it would be wise to prioritize them for your own convenience, as a facilitator. If you are running out of time towards the end you can then ensure you are covering the most important topics during the time you have available after the initial portion of the exercise.
- Be sure to stress that diversity is a plus for team creativity and finding new solutions. The objective of this activity is to help work out some of the downsides of diversity without marginalizing any one or group or impose judgement.
Non-homogeneous teams may be tougher to manage than homogeneous teams, but the pay-off in creating new and innovative team solutions coupled with individuals learning new skills and perspectives from other team members can be very rewarding. As a team leader or facilitator you just need to make sure you have the right tools, such as this activity, available to help non-homogeneous teams succeed.