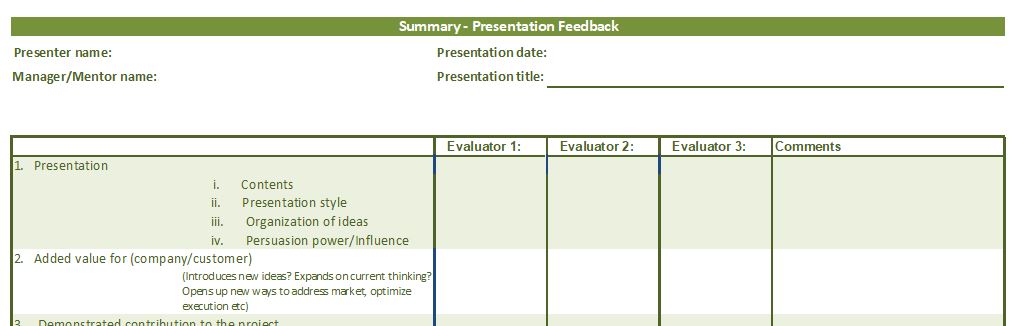
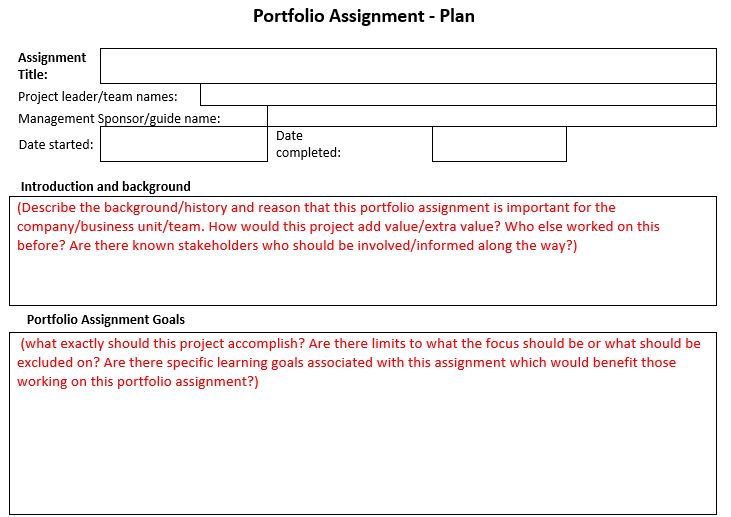
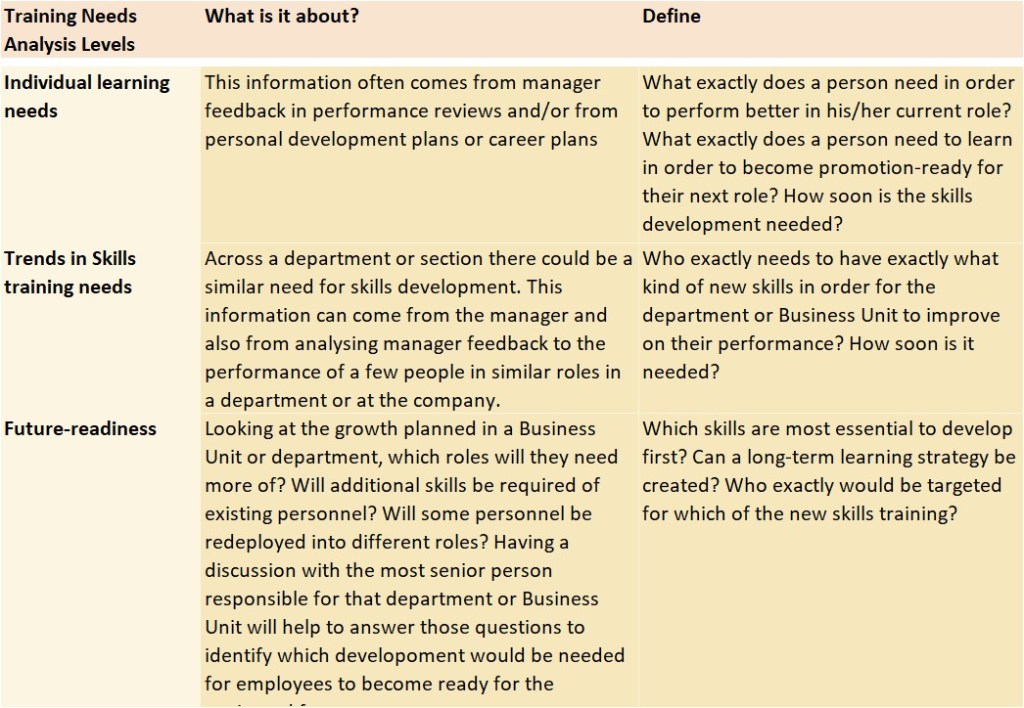
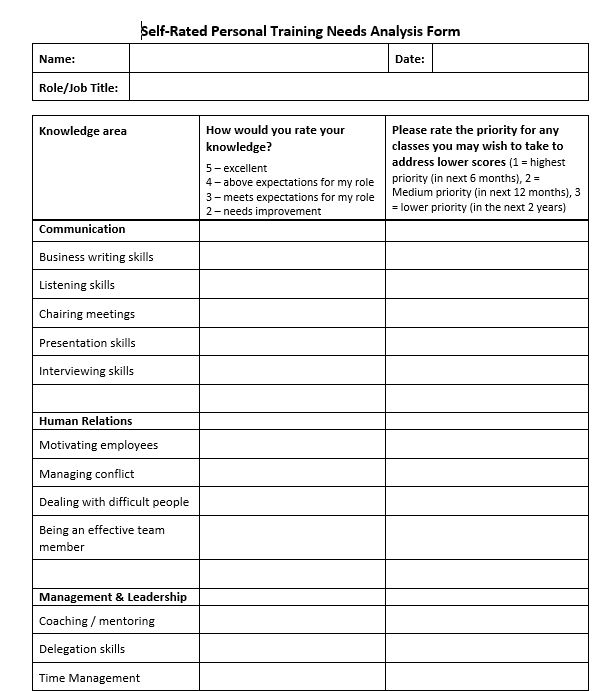
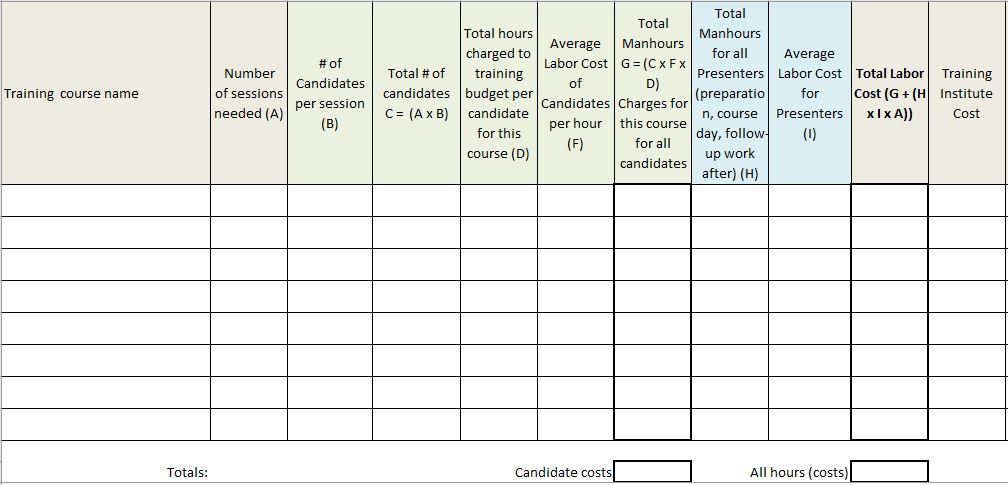
One area that often causes misunderstandings and frustrations in the workplace is when two employees have different interpersonal styles and ways of communicating and they do not get along. Being different from each other mostly means that they do not understand why the other party is doing and saying things in the manner that they do. Most of us do have the ability to make small changes to how we do or say things in order to improve collaboration and interfacing with others and this resource can help by creating awareness, which is the first step towards improvement.
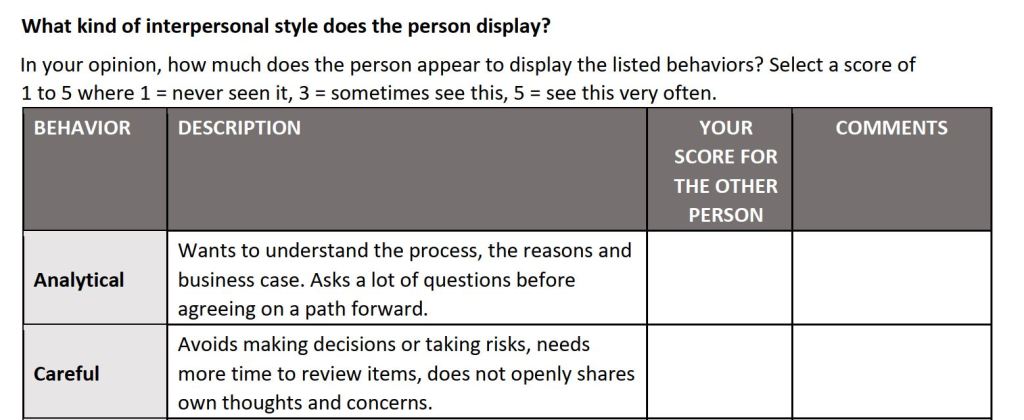
The downloadable document I am sharing can be used for reviewing relationships with customers, other employees, work-related contacts, and even friends or loved ones. It helps you reflect on the interpersonal style that the other person displays in his or her behaviors. Building on this awareness this resource enables you to be more mindful of the best ways to interact with that specific person to have a better relationship with him or her.
Once you have awareness of how you can improve interpersonal relationships with specific people it may still be difficult to make changes to your own behavior for the betterment of the relationship. Should you get stuck once you have done the first part of the exercise, consider asking others for ideas on how you can best approach improvement in the key aspects you came up with. Depending on the current relationship you have with the person you focused on, you may be able to ask him or her directly. For example: “I noticed that you are very detail-oriented. Can you help me understand how I can better provide you with what you need in order for you to feel comfortable with my contribution on the projects that we are working on together?”
Uses for this resource include:
- Own reflection and then taking action to improve on some of your interpersonal relationships.
- Discussions with your coach on how to deal with some difficult individuals that you often work with.
- Team-building – ask each team member to rate themselves on the items shown and then share with each other as a way to get to know each other better and improve interpersonal relationships on the team. (advocating).
- Team feedback – Depending on the time you have available and the size of the team you may also ask each team member to map out each other team member using this resource. This means each person gets feedback from the entire team on how each team member sees them. The outcome could magnify self-awareness in the team and drive interpersonal relationship improvements across the entire team.
Misunderstandings can lead to a lot of misalignments between team members and can result in rework, which is a waste every project should avoid. Better interactions with others make the workday more fun and go a long way towards employees feeling more productive and effective at work.